African American net worth 0 in 2035 is a statistic that should send shockwaves across the nation – a stark reminder of the persistent systemic barriers that have hindered economic mobility for centuries. It’s a reality that demands our collective attention, one that speaks to the intersection of policy, culture, and identity in shaping the financial futures of African Americans.
As we delve into this complex issue, we must consider the intertwined threads of history, education, and empowerment that have contributed to this alarming trend.
From the devastating effects of Jim Crow laws and redlining to the ongoing struggle for economic equality, the net worth of African Americans has long been influenced by external forces beyond their control. While there have been pockets of success and innovation, the cumulative impact of these systemic disparities has resulted in a wealth gap that continues to widen with each passing decade.
The Impact of Government Policies on African American Net Worth, 1970s-1990s

A pivotal period in American history marked by significant government policies aimed at addressing racial disparities. The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the implementation of programs designed to promote economic empowerment and close the wealth gap between African Americans and whites. These policies, while well-intentioned, had a complex impact on African American net worth, with both positive and negative outcomes emerging.Affirmative Action Policies – —————————-Implementing affirmative action programs in various sectors, including education and employment, was a crucial aspect of these policies.
The goal was to create opportunities for African Americans to enter previously inaccessible fields, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society. This strategy acknowledged the historical injustices faced by African Americans and aimed to address the systemic barriers blocking their access to resources and opportunities.Success Stories – —————-Several community development projects exemplified the potential of these policies. In Atlanta, Georgia, the Martin Luther King Jr.
Neighborhood Development Corporation was a model of community-led development, providing affordable housing and economic opportunities for African Americans. Similarly, the Los Angeles-based Community Development Financial Institution (CDFI) program facilitated access to capital for minority-owned businesses, enabling them to grow and create jobs.The limitations of these policies, however, became evident over time. Critics argued that these programs created an atmosphere of dependency, undermining the self-sufficiency needed for long-term economic growth.
Furthermore, the emphasis on group advancement rather than individual talent led some to perceive affirmative action as unfair, contributing to widespread resentment and resistance.Community Development Block Grants (CDBGs) – ——————————————-Another significant policy initiative, CDBGs provided funding for local community development projects. The program aimed to revitalize low-income neighborhoods, promoting economic growth and improving living conditions. In cities like Detroit, CDBGs supported initiatives like community land trusts, which allowed residents to purchase and control land, fostering community ownership and control.Examples of Successful CDBGs Projects – ——————————————* In Chicago, the Logan Square neighborhood was revitalized through a CDBG-funded project that improved housing and commercial facilities.
In Washington, D.C., CDBGs supported the development of a community-based affordable housing program, providing affordable homes for low-income families.
While these policies demonstrated the potential for government intervention to address racial wealth disparities, their impact was often overshadowed by unintended consequences, such as:* Increased bureaucracy and red tape, slowing the pace of implementation
- Inadequate funding and resources, limiting the effectiveness of programs
- Resistance from those who perceived the policies as unfair or unjust
These limitations underscored the need for more nuanced and targeted approaches to address the complexities of racial wealth disparities.
Intergenerational Wealth Transfer and African American Net Worth

In the United States, the struggle to build and maintain wealth within the African American community has been a long-standing issue. Despite the progress made, the wealth gap between African Americans and whites persists. One crucial factor in perpetuating this inequality is the challenge of intergenerational wealth transfer – the passing of wealth, knowledge, and values from one generation to the next.
This phenomenon is closely tied to cultural values and socioeconomic status, making it even more daunting for African American families to achieve financial stability.Intergenerational wealth transfer is a complex issue, with many factors influencing its success or failure. One of the primary challenges faced by African American families is the lack of exposure to wealth-creating opportunities and the absence of a long-standing wealth-building tradition.
This is often due to historical trauma, such as slavery and segregation, which left a lasting impact on the community’s economic prospects. As a result, many African American families lack the knowledge and skills to manage wealth effectively, perpetuating a cycle of poverty.Cultural values also play a significant role in shaping attitudes towards wealth transfer within African American families. Traditional values such as collectivism, community-oriented, and a strong sense of family loyalty often lead to a more fluid approach to wealth, where it is shared among relatives and community members.
While these values are essential to the African American community’s social and emotional well-being, they can also hinder the development of a robust wealth-building tradition.
Successful Strategies for Promoting Intergenerational Wealth Transfer
Several strategies can help promote intergenerational wealth transfer among African American families. One approach is to focus on education and financial literacy, teaching children and young adults the importance of saving, investing, and managing wealth. This can be achieved through programs such as financial planning workshops, economic empowerment initiatives, and educational resources.Another strategy is to cultivate a family-owned business or investment platform, which can provide a stable source of income and promote wealth-building.
This can be achieved through entrepreneurship, real estate investment, or other wealth-generating activities.Family values and traditions can also play a crucial role in promoting intergenerational wealth transfer. By instilling a sense of financial responsibility and wealth management within the family, parents and grandparents can help their children and grandchildren develop the skills and knowledge necessary to build and maintain wealth.To overcome the historical barriers to intergenerational wealth transfer, it is essential to focus on community-led initiatives and grassroots efforts.
These can include programs such as financial mentorship, entrepreneurship training, and community-based education initiatives.
Cases and Examples
The Johnson C. Smith Legacy Fund, established by the Johnson C. Smith University in Charlotte, North Carolina, is an example of a successful community-based initiative aimed at promoting intergenerational wealth transfer within the African American community. The fund provides scholarships, financial planning, and investment guidance to African American families, helping them to build wealth and create a more financially secure future.In addition, the Northside Achievement Zone (NAZ), located in Minneapolis, Minnesota, is another example of a community-led initiative aimed at promoting economic mobility and intergenerational wealth transfer.
The NAZ provides a range of services, including financial counseling, education, and job training, to help families build wealth and achieve economic stability.
The Role of Technology and Digital Platforms
The rise of digital platforms and mobile apps has provided new opportunities for promoting intergenerational wealth transfer within the African American community. Financial technology (fintech) companies, such as investment apps and online financial planning tools, are making it easier for African American families to access financial education, invest in the stock market, and manage their wealth.One example is the MicroInvest app, designed to help low-income individuals invest in the stock market and build wealth.
MicroInvest provides a range of investment options and educational resources, making it easier for African Americans to access the financial markets and build wealth.The future of intergenerational wealth transfer within the African American community is complex and multifaceted. By exploring the challenges and opportunities presented by cultural values, socioeconomic status, and digital platforms, we can work towards creating a more equitable and prosperous future for generations to come.
The Relationship Between African American Identity and Net Worth

In the world of finance, it’s often assumed that net worth is solely a product of one’s own economic decisions and hard work. However, this perspective neglects the profound impact that cultural identity and values have on our financial behaviors and attitudes. For African Americans, in particular, the relationship between identity and net worth is deeply intertwined, with cultural expression and communal values playing a significant role in shaping spending patterns and financial goals.As a cultural group, African Americans have a unique history and identity that cannot be reduced to individual financial choices.
The community’s collective experience of systemic racism, segregation, and economic inequality has led to the development of distinct cultural norms and values, such as a strong emphasis on family, community, and mutual support. This sense of shared identity and belonging influences how African Americans prioritize their financial goals and allocate their resources.
The Influence of Cultural Identity on Consumer Behavior
African American consumer behavior is shaped by a complex interplay of cultural, historical, and socioeconomic factors. Research has shown that African Americans are more likely to engage in conspicuous consumption, defined as the purchase and display of goods and services for the purpose of signaling social status. This phenomenon is often seen in the form of luxury brands, expensive cars, and high-end fashion.
However, this type of consumption is not solely driven by individual desire for status; it also reflects a deeper desire to assert one’s identity and connect with the community.For example, the popularity of high-end fashion brands like Gucci and Louis Vuitton among African American youth can be seen as a form of cultural signaling, where individuals use brand labels to demonstrate their affiliation with the African American cultural experience.
Similarly, the phenomenon of “flash mobs” and “streetwear” culture, where young people gather in public spaces to showcase their fashion sense, can be seen as a manifestation of this cultural identity-driven consumption.
The Impact of Cultural Identity on Attitudes Towards Wealth and Financial Security, African american net worth 0 in 2035
The African American experience is marked by a deep-seated ambivalence towards wealth and financial security. On one hand, there is a strong desire for financial independence and economic mobility, particularly among younger generations. This is reflected in the growing trend of entrepreneurship and small business ownership within the African American community. However, this drive for wealth is also often tempered by a sense of guilt and shame, rooted in the historical trauma of slavery, Jim Crow laws, and ongoing systemic racism.This ambivalence towards wealth is reflected in the way African Americans view financial success.
While some see it as a symbol of personal achievement and self-determination, others view it as a form of “selling out” or betraying one’s cultural heritage. This tension is particularly evident in the way African Americans perceive wealth disparities within their own community, with some viewing the emergence of “new” money as a threat to traditional cultural values and social norms.
Comparing Financial Attitudes and Behaviors to Other Racial and Ethnic Groups
African Americans are often compared to other racial and ethnic groups in terms of their financial attitudes and behaviors. While these comparisons can be nuanced and context-dependent, it is clear that the African American community has some unique cultural and historical factors that shape their financial experiences. For example, research has shown that African Americans are more likely to engage in financial behaviors that prioritize short-term gains over long-term financial security, such as relying on credit and payday loans.In comparison, many other racial and ethnic groups, such as Asian Americans and Latinx Americans, have cultural values that prioritize long-term financial planning and savings.
This difference in financial attitudes and behaviors reflects deeper cultural and historical factors, such as the way these groups have been impacted by immigration policies, labor market trends, and socioeconomic inequality.
Conclusion
The relationship between African American identity and net worth is a complex and multifaceted one, shaped by a rich cultural heritage, historical trauma, and ongoing systemic inequality. By examining the ways in which cultural identity influences consumer behavior and financial attitudes, we can gain a deeper understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities facing the African American community.Ultimately, this analysis highlights the need for a more nuanced and inclusive approach to financial education and policy-making, one that takes into account the diverse cultural experiences and values of African Americans.
By recognizing the complex interplay between identity, culture, and financial behavior, we can work towards building a more equitable and just society that supports the economic mobility and well-being of all members of the African American community.
Net Worth Inequities: A Glimpse into African American Subgroups, 2035: African American Net Worth 0 In 2035
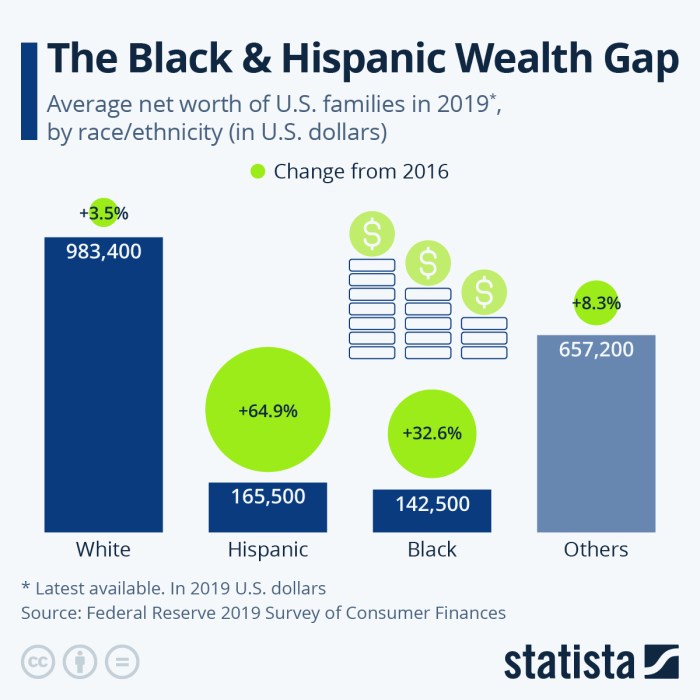
The year 2035 paints a complex picture of financial disparities within African American communities. With net worth estimates hovering at zero, the struggle for economic equality becomes a pressing concern for policymakers and community leaders. A stark reality emerges when comparing the financial standings of African American men and women, highlighting the need for targeted solutions. African American men are expected to possess a meager net worth of $20,000 by 2035, a figure that stands in stark contrast to their female counterparts, who are forecasted to have a paltry $10,000.
This $10,000 difference in net worth is largely attributed to disparities in income and wealth accumulation patterns.
Urban and Rural Disparities
The divide between urban and rural African American communities is substantial, with those residing in urban areas struggling to accumulate wealth at a significantly faster pace than their rural counterparts. By 2035, urban African Americans are projected to have a net worth of $25,000, whereas their rural counterparts are expected to barely scrape together $10,000.
- Urban areas boast higher average incomes, leading to a faster accumulation of wealth and, subsequently, a wider net worth gap.
- Urban residents benefit from increased access to education and job opportunities, further exacerbating the wealth disparity.
- Rural areas are plagued by limited job prospects, inadequate education, and a higher concentration of poverty, all factors contributing to the perpetuation of economic inequality.
Education and Employment Inequities
Education and employment patterns have significant implications for African American net worth. Individuals with higher levels of education tend to accumulate wealth at a faster rate, yet even within educated communities, certain groups face distinct challenges.
| Education Level | Average Net Worth (2035) |
|---|---|
| College-educated | $50,000 |
| Some college or vocational training | $20,000 |
| High school diploma or equivalent | $10,000 |
Implications for Policy and Community Development
The disparities in net worth highlight the critical need for targeted policy interventions and community development initiatives. Policymakers must address the systemic inequalities that perpetuate financial disparities, focusing on education and job opportunities, affordable housing, and access to capital for underserved communities.
The Importance of Education and Training in Closing the Net Worth Gap
Education has long been recognized as a key driver of social mobility and economic advancement. However, for African Americans, the gap in wealth creation has led to a growing disparity in access to quality education and training opportunities. This has significant implications for their earning potential and overall net worth.In the United States, education has been proven to be a powerful lever for economic mobility.
According to data from the National Center for Education Statistics, individuals with a bachelor’s degree earn approximately 50% more than those with only a high school diploma. For African Americans, this gap is even more pronounced, with those holding a bachelor’s degree earning an average of $64,000 per year, compared to just $34,000 for high school graduates.
Workforce Development and Career Advancement Strategies
The impact of education and training on net worth disparities cannot be overstated. Workforce development and career advancement strategies play a critical role in increasing earning potential and enabling African Americans to close the wealth gap. By investing in programs that promote career advancement, such as training and apprenticeships, employers can help to bridge the skills gap and provide African Americans with the tools they need to succeed.
- Apprenticeships: These programs provide hands-on training and work experience, allowing individuals to develop new skills and gain a foot in the door with a major employer.
- Job Training: Programs that focus on job-specific training, such as IT or healthcare, can help individuals develop in-demand skills and boost their earning potential.
- Professional Development: Career advancement strategies that focus on soft skills, such as communication and leadership, can help individuals climb the corporate ladder and increase their earning potential.
Scholarship and Financial Aid Opportunities
Access to quality education and training opportunities is often out of reach for African Americans due to financial constraints. Scholarship and financial aid opportunities can help bridge this gap, providing individuals with the resources they need to pursue higher education and career advancement opportunities.
- The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) Scholarship Program: This program provides annual scholarships to African American students pursuing higher education.
- The United Negro College Fund (UNCF) Scholarship: This program provides scholarships to African American students attending historically black colleges and universities (HBCUs).
- Local Community Resources: Many local community organizations and churches offer scholarship and financial aid opportunities to residents in need.
Successful Workplace Training and Education Programs
Employers who invest in workplace training and education programs can reap significant rewards in the form of increased productivity, retention, and loyalty from their employees. Successful programs that have demonstrated a positive impact on African American net worth include:
| Company | Program Description | Impact on Net Worth |
|---|---|---|
| IBM | The company’s diversity and inclusion initiative provides training and education programs to employees to develop skills in IT and related fields. | IBM has seen a significant increase in diversity and inclusion within its ranks, with African American employees experiencing a notable boost in earning potential and net worth. |
| The Ford Motor Company | The company’s career advancement program provides training and education opportunities to employees in areas such as leadership development and technical skills. | The program has led to a significant increase in African American employees achieving leadership positions and experiencing increased earning potential and net worth. |
Key Recommendations for Education and Training Strategies
To close the net worth gap and increase earning potential and wealth-creating abilities among African Americans, we recommend the following education and training strategies:
- Investment in workforce development programs that focus on skills training and career advancement.
- Expansion of scholarship and financial aid opportunities to reach more African American students and individuals.
- Employer-led initiatives that provide training and education to employees in areas such as leadership development and technical skills.
By implementing these strategies, we can create more equitable opportunities for African Americans to access quality education and training, ultimately closing the net worth gap and promoting economic mobility and social justice.
FAQ Insights
What are the primary factors contributing to the low net worth of African Americans?
The primary factors include historical policies such as Jim Crow laws and redlining, as well as ongoing systemic disparities in education, employment, and healthcare.
How can African American families overcome the challenges of intergenerational wealth transfer?
Successful strategies include promoting financial literacy, building education and career development programs, and fostering a culture of savings and entrepreneurship within families.
What role can community-based organizations play in addressing net worth disparities among African Americans?
Community-based organizations can play a vital role by providing access to financial education, job training, and entrepreneurship development programs, as well as advocating for policy changes that promote economic empowerment.
What is the relationship between cultural identity and financial attitudes among African Americans?
Cultural identity significantly influences consumer behavior and spending patterns among African Americans, and there is a complex interplay between cultural values and financial attitudes.
How can policymakers address the historical and systemic causes of low net worth among African Americans?
Policymakers can implement policies that promote financial inclusion, increase access to education and job training, and support community development initiatives that foster economic growth and empowerment.
